RAM (Random Access Memory) is a crucial component of any gaming PC. Adding more RAM can improve system responsiveness and improve frame rates compared to systems with less memory.
Read on to find out how RAM works, how to find compatible modules, and how much memory you really need for gaming.
How does RAM work?
The purpose of RAM is to store the short-term data that a PC needs to run properly. But unlike a hard drive or SSD (solid-state drive), which store data indefinitely, RAM resets every time the system restarts.
RAM is “volatile memory”; That is, unlike a “non-volatile” hard drive or SSD, it only stores data when powered. Programs are temporarily loaded into RAM while in use, but reside permanently on a storage drive (until erased).
Computers need quick access to temporary data to run programs and tasks. For example, modern PC games need to retrieve art assets quickly. Games read and write data to RAM, which is many times faster than accessing data from a storage device.
Which RAM is compatible with your motherboard?
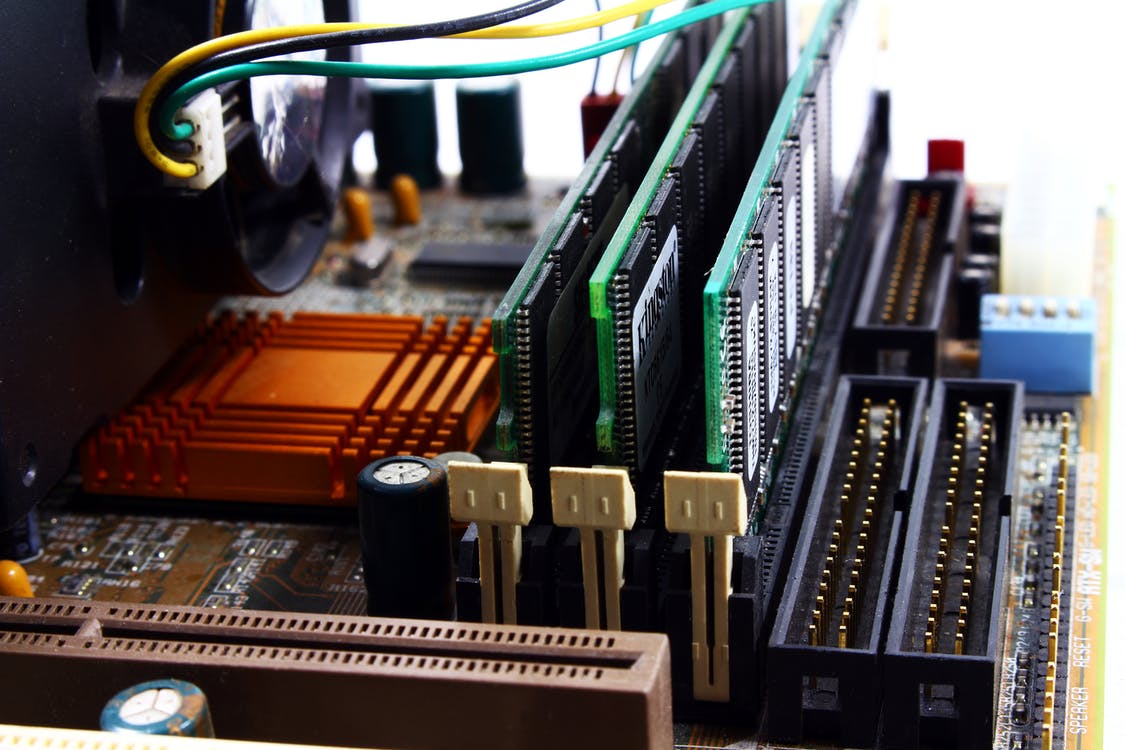
Before thinking about RAM capacity and frequency, you should make sure that the RAM is compatible with your motherboard and processor. The wrong type of module just won’t work, and RAM with the wrong specs for your PC may provide underperformance.
module type
RAM comes in the form of sticks or memory modules that snap into memory slots on the motherboard. RAM that is not compatible with your system will either not fit or function properly.
Mainboards of modern computers support DDR4 RAM. DDR4 should not be confused with DDR3, the previous generation of SDRAM. They are not interchangeable and you cannot replace 8GB DDR3 with 16GB DDR4 for example.
DDR4 and SDRAM
Computers use a type of RAM called SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory). “Synchronous” DRAM is synchronized with the frequency of the processor. SDRAM has improved over time, offering benefits such as lower power consumption, faster transfer rates, and more stable data transfer.
DDR4-SDRAM is the current standard of modern computers. DDR4 stands for “Double Data Rate 4” and is the fourth generation of DDR technology that replaces the SDR (Single Data Rate) SDRAM. DDR4 offers faster data transfer rates, larger capacities and lower voltages than the previous generation.
If you’re building a new PC or upgrading RAM in a relatively new system, you’re probably familiar with the current standard of DDR4 SDRAM.
Why isn’t DDR4 backwards compatible? Because he u. has different timings (see below), voltage and pin count characteristics. To prevent accidental installation, the notch is behind a different pin on DDR4 modules than on DDR3 modules. This ensures that they cannot be pushed into DDR3 slots.
There are a few easy ways to find compatible memory. Consult your system or processor documentation, run a utility to profile your system, or use an online storage compatibility tool.
form factor
DIMM – (Dual In-Line Memory Module) sticks are larger RAM modules designed for desktop motherboards.
SO-DIMM – (Small Outline Dual In-Line Memory Module) are smaller modules for laptops, Intel® NUC Mini PCs, and some small form factor (SFF) Mini-ITX motherboards.
Important RAM specifications
- Capacity : Measured in gigabytes (GB). The higher the capacity, the more data applications can store. With higher capacities, more applications can run simultaneously and games can store larger amounts of temporary data.
- Speed : Measured in mega-transfers per second (MT/s); often also speed in megahertz (MHz), but that’s a different unit of measure than clock frequency. Higher speed means faster response to read and write requests, and therefore increased performance.
How much RAM do I need for gaming?
Depending on. Do you plan on playing games in targeted sessions, or do you tend to stream and multitask?
For playing AAA titles, 8GB is considered the basic requirement. However, the demands on the RAM are increasing. For example, Red Dead Redemption 2 recommends 12GB of RAM for optimal performance, while Half-Life: Alyx states 12GB as the minimum requirement. So if you want enough headroom to keep playing new releases in the future, 16GB of RAM is recommended.
If you want more than just gaming, consider 32GB. This gives you the ability to live stream, have group chats on Discord, and keep YouTube or Twitch running in the background.
If you have the budget and need more RAM (for 3D modeling or other professional applications), Windows 10 Home and the latest Intel® Core™ i9 processors support up to 128GB. This is in “Max. Memory Size” under the processor’s memory specifications.
What RAM speed do I need?
Make sure you get the balance between capacity and speed. It’s likely that 32GB of slow RAM isn’t ideal, but 4GB of fast RAM isn’t ideal either.
DDR4 RAM speeds start at around 1600MHz, however these speeds are considered slow by today’s standards. For example, the Intel® Core™ i9-10900 processor supports 2933 MHz using the standard specifications.
When gaming, it is beneficial to use RAM with high rated speeds. Although not as big an impact as upgrading the processor or graphics card, faster RAM can improve gaming performance and frame rates.
Performance improvements vary from game to game: some games show a noticeable improvement, others barely. It’s a good idea to check the average frames per second benchmarks to see if it’s worth upgrading.
In addition to improving frame rate, faster RAM can improve frame duration or frame rate stability. This is reflected in the low values of 1% and 0.1% in the benchmarks (average values of the slowest 1% and 0.1% of the recorded frames).
Aside from frame rates, faster RAM can also improve other areas of system performance, such as: B. the reduction of loading times.
Other considerations
installation
RAM is usually purchased in sets of two or four modules (e.g. 2 16GB modules or 4 8GB modules). Before you buy a kit, check how many memory slots your motherboard has.
Desktop PCs usually have four slots, laptops usually two. High-performance PCs and workstations may have eight or more, while specific configurations such as NUCs and SFFs vary in the number of slots.
If you are planning to upgrade a laptop’s RAM, make sure the RAM is accessible and not soldered to the motherboard. In some cases, a laptop’s RAM cannot be replaced.
If you’re planning to upgrade a desktop PC, it’s a good idea to leave some memory slots open for future expansion. For example, if you install a set of 2 16GB modules instead of a set of 4 8GB modules on a desktop PC, you will have two slots available for future upgrades.
To take advantage of the increased bandwidth of dual-port RAM, it is recommended that you install at least one pair of RAM modules in symmetric slots (usually color-coded). The modules must have the same capacity and ideally the same speed: if the speeds do not match, the module with the slower speed will set the pace.
What is Dual Port RAM?
Many modern computers offer dual port memory. In two-channel mode (interleaved mode), the memory controller of the CPU can exchange data with the RAM via two channels and read and write to two memory sticks at the same time. This increases the available bandwidth.
Dual channel mode is automatically enabled on most motherboards with only two DIMM slots. However, when using two sticks in a four-slot motherboard, the memory must be installed in the same channel. Slots are often color-coded, but can be either staggered or side-by-side. For more detailed instructions, please refer to your motherboard documentation.
For best performance, make sure each memory stick has the same speed, capacity, and timing. If possible, avoid combining and merging different module specifications.
memory timing
RAM speed isn’t the only way to measure performance.
RAM timings are a measure of the latency or delay before the RAM can execute commands that are issued. Memory timings are given as a series of numbers, e.g. B. 16-18-18-36, which can be found on the factory label of the module.
Each number corresponds to a specific test. For example, the first number is the Column Address Strobe (CAS) latency—the number of clock cycles it takes for the memory module to return a record after a request from the memory controller.
Comparing RAM modules based on timings can be complicated. For example, the CAS latency only gives the total number of cycles; however, the duration of each cycle also plays a role in assessing responsiveness. For example, DDR3 memory typically has lower CAS latency than DDR4, but is worse due to its slower clock speed.
Memory timings are not usually a high priority for gaming PCs. Timings are of interest to over clockers who can manually lower timings in the BIOS and then test for stability. If successful, you can improve the performance of your existing RAM.
For most gaming PC users, RAM capacity and speed are the most important considerations.
Overclocking 1 RAM
If you’ve bought powerful RAM, overclocking can help you go beyond the stock specs. The easiest way to achieve this is with Intel® Extreme Memory Profile (Intel® XMP).
When an Intel® XMP profile is selected in the BIOS of a supported motherboard, the voltage, timing, and frequency are adjusted to increase performance. These predefined settings have been tested and certified for stability.
In addition, with some mainboards, the memory profiles can be optimized and the settings can be precisely adjusted manually via the BIOS.
To get started, please read this detailed guide on overclocking RAM first .
Aesthetics and cooling
Memory heatsinks can make your setup more attractive. However, they are often purely aesthetic.
RAM generates heat just like any other component; however, it only runs very hot when operating at unusually high speeds. Unless you ‘re serious about overclocking your RAM, you can skip this heatsink info . However, as with any component, one should always ensure proper airflow for the memory.
Memory modules with RGB lighting are also used for aesthetics and can make your system appear more visually appealing. Just make sure that the RGB memory sticks you choose are compatible with your particular motherboard brand.
What Kind of RAM is Right for Your Gaming PC?
Ultimately, the amount of RAM you need for gaming depends on your budget and use case. Before you buy, make sure the memory specifications are right for your unique needs.
It’s important to balance memory with the rest of your system’s components, as they all play a role in determining overall performance levels.
To learn more about balancing the components in your system , read our balanced PC guide.


